The Value of U.S.–China Interdependence: A Deep Dive into Economic and Strategic Connections
The relationship between the United States and China is a complex web of interdependence that has significant implications for both nations. Despite tensions, their economies and policies are intricately linked, making it difficult for either country to act unilaterally without affecting the other. This analysis explores the mutual dependencies under various sectors, showcasing how intertwined the two superpowers are.
The Value of the U.S. to China
1. Capital Markets
Chinese companies rely heavily on U.S. financial markets to raise capital. Despite increasing restrictions imposed by the Biden administration, Chinese-listed firms raise approximately $56 billion annually in funding from U.S. markets and hedge funds. Though lower than the peak of $91 billion in 2017–18, this figure remains significant compared to other regions like the EU ($161 billion) and Japan ($83 billion).
To put this into perspective, Chinese companies raised $76 billion domestically and in Hong Kong this year—42% of which came from U.S. capital markets. This demonstrates the critical role U.S. markets continue to play in financing Chinese businesses.
2. Advanced Equipment and Technology
China is on an aggressive path toward self-sufficiency in advanced technologies. While the country's indigenization rate has grown from 7% in 2012 to 40% in 2024, it still relies on imports for 60% of advanced technology applications. This dependency contrasts sharply with the U.S., which depends on other nations for only 10% of its technology needs.
Remarkably, China’s progress has been rapid—doubling its indigenization rate from 20% in 2019 to 40% in just five years. Despite ongoing U.S. sanctions and export restrictions, China continues to source significant technology imports from the Collective West, highlighting its resilience and strategic adaptability.
The Value of China to the U.S.
1. Value Addition to the Economy
Chinese goods contribute an astounding $2.5 trillion in value addition to the U.S. economy annually, accounting for 20% of the larger retail consumption in the U.S. No other country comes close—Canada, Mexico, the EU, India, and Japan collectively contribute less than $2 trillion.
China's dominance in this sector underscores its vital role in the affordability and availability of consumer goods in the U.S. market.
2. Corporate Profits and Earnings
U.S. corporations derive a significant portion of their profits from the Chinese market. In 2024, 24.95% of profits for U.S.-registered corporations came from China, second only to domestic profits (42.27%) and far exceeding the EU (17.13%). This translates to $1 in every $4 in corporate profits originating from China.
In contrast, Chinese corporations earn just 4% of their profits from the U.S., with the majority (59.25%) coming from mainland China and Hong Kong.
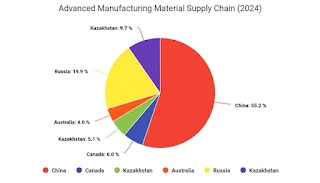
3. Supply Chain Dependence
The U.S. manufacturing sector relies heavily on China's supply chain infrastructure. Together, China and Russia control 85% of all raw materials required for advanced manufacturing, while China alone accounts for 43% of these supply chain needs.
Moreover, 60% of all processing components necessary for advanced manufacturing in the U.S. come from China and Russia. This dependence underscores the difficulty of reducing reliance on Chinese supply chains without significant disruption to U.S. manufacturing.
4. Fentanyl Control
The U.S. has seen a troubling rise in fentanyl overdose deaths, with a 260% increase between 2021 and 2023. This spike was linked to China’s relaxation of end-user vetting procedures during that period. However, in 2024, overdose cases decreased by 44% as China reinstated these procedures.
China’s control over fentanyl exports gives it leverage in its relationship with the U.S., as any lapse in regulation could lead to devastating consequences for public health in America.
Key Takeaways and Conclusion
The U.S.–China relationship is defined by mutual dependence across economic, technological, and strategic dimensions. For China, access to U.S. capital markets and advanced technology remains critical to its economic growth and technological innovation. For the U.S., Chinese goods, supply chains, and market access significantly bolster its economy, corporate profits, and manufacturing capabilities.
Both nations have leverage over one another, with China holding strategic cards such as its dominance in the supply chain and its role in regulating fentanyl exports. The U.S., on the other hand, has the upper hand in financial markets and technology development.
This interdependence is unprecedented in modern history. For the U.S., such reliance on another nation is a rarity, especially for a global superpower. For China, maintaining ties with the U.S. is essential to its continued ascent as a global economic powerhouse.
Frequentyl Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can the U.S. reduce its supply chain dependency on China?
Diversifying suppliers, investing in domestic manufacturing, and strengthening trade relations with other countries like India and Vietnam could help the U.S. reduce its reliance on China. However, such transitions require significant time and investment.
What would happen if the U.S. and China decoupled economically?
An economic decoupling would have severe repercussions for both nations. The U.S. would face supply chain disruptions, increased production costs, and inflation, while China would lose access to vital capital markets and advanced technologies, stalling its economic growth.
What are the main differences in how the USSR, USA, and China define freedom?
The USSR focused on collective control over individual liberty, while the USA emphasized individualism and free speech. China defines freedom through respect for authority and societal harmony, prioritizing collective well-being over personal rights.




Post a Comment